
Nucleic acids are the most common examples (DNA and RNA). It is found in cellulose.Ī phosphodiester bond is a covalent link in which the two OH groups of the phosphoric acid, (HO) 2P(=O) 2, form two separate ester bonds between the OH containing carbon number 5’ on one sugar unit and OH of carbon 3’ of another sugar unit, that is –C-OH, of two sugar molecules. Beta-Glycosidic bond: The two bond-forming atoms in beta-glycosidic bonds are orientated in opposing planes and have differing stereochemistry.Alpha-Glycosidic bond: The atoms that make up an alpha-glycosidic bond are all orientated in the same plane, making them stereochemically similar.N-Glycosidic Bond: A chemical reaction occurs when the carbonyl group of a carbohydrate molecule reacts with the amino group (-NH 2) of a non-carbohydrate molecule to create this bond.O-glycosidic bond: It’s the most common glycosidic bond in which the carbonyl group of carbohydrates interacts with the hydroxyl group of another chemical to form an O-glycosidic bond.The reaction is often referred to as dehydration or condensation reactions. A water molecule is eliminated whenever a glycosidic link is formed. Glycosidic BondĪ glycosidic bond is produced when two neighbouring monosaccharides join together to form disaccharides or polysaccharides. An amide is generated as a result of the reaction. Peptide bonds can form at both N-terminal and C-terminal. Polypeptide chains of amino acids make up proteins. A water molecule is eliminated when a peptide bond is formed, and the reaction is also called a condensation reaction. An amide group, or peptide group, is a four-atom functional group with the formula C (=O)NH. The molecule that results is known as an amide. A peptide bond is an amide bond (-CONH) formed by the –NH 2 and –COOH groups of neighbouring amino acids. The amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains. Major bonds present in biomolecules are discussed below: Peptide Bond E.g., Hydrogen bond, hydrophobic interaction, disulphide bond, ionic interaction. Proteins and nucleic acids contain most of them. These bonds are primarily responsible for maintaining biological molecules’ secondary, tertiary, and higher structures. In biological molecules, secondary bonds are the transient forces of attraction that form when particular atoms or groups approach near together. Secondary Bonds: These are formed due to electrostatic attraction developed due to the orientation of molecules in space.
E.g., Glycosidic bond, Peptide bond, ester bond. These are the permanent bonds that either consume or release energy while forming. They may form by a reversible or irreversible chemical reaction. Primary Bonds: These are covalent bonds formed due to sharing of electrons.The chemical bonds can be categorised into two in the case of biomolecules:

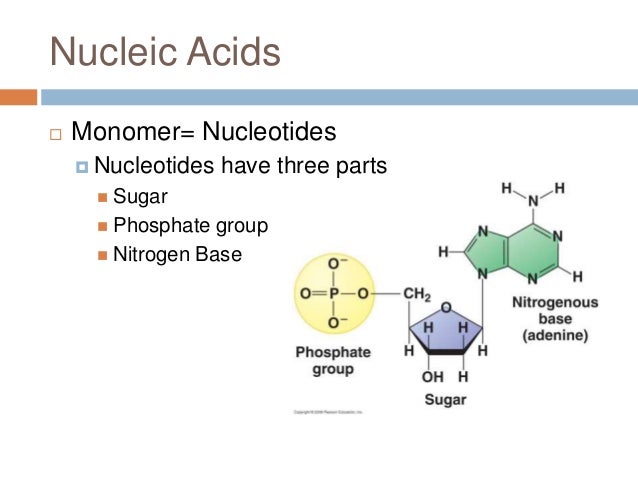
Ribonucleotide: Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogenous base(A,U,G,C)įig: Various Biomolecules Important Bonds Present in Biomolecules A list of significant polymers are given below: Polymerĭeoxyribonucleotide: Sugar + Phosphate + Nitrogenous base (A,T,G,C) Each complex biomolecule is composed of a small monomer. The nature of bonds connecting the monomer units of polymers is dependent on the chemical nature of the constituent monomers. Depending on its chemical composition, various types of bonds are used to hold the monomeric unit together. From Monomer to PolymerĪ polymer is a material made up of many small molecules joined together by means of a chemical bond to form a larger molecule. Each of these monomer types is important in the survival and development of life, and each can be synthesised abiotically. Simple sugars, amino acids, nucleotides, fatty acids and glycerol are the four main types of monomers. Learn About Rocks Here What are Monomers?Ī monomer is a simple molecule having two or more binding sites that create covalent bonds with other monomer molecules to produce a macromolecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
